The ovaries are the organs of the female reproductive system that produce eggs. There are two of them, buried deep in the woman's pelvis on either side of the uterus, near the tip of the fallopian tubes.
Every year, nearly a quarter of a million women worldwide are diagnosed with ovarian cancer and the disease causes 140,000 deaths.
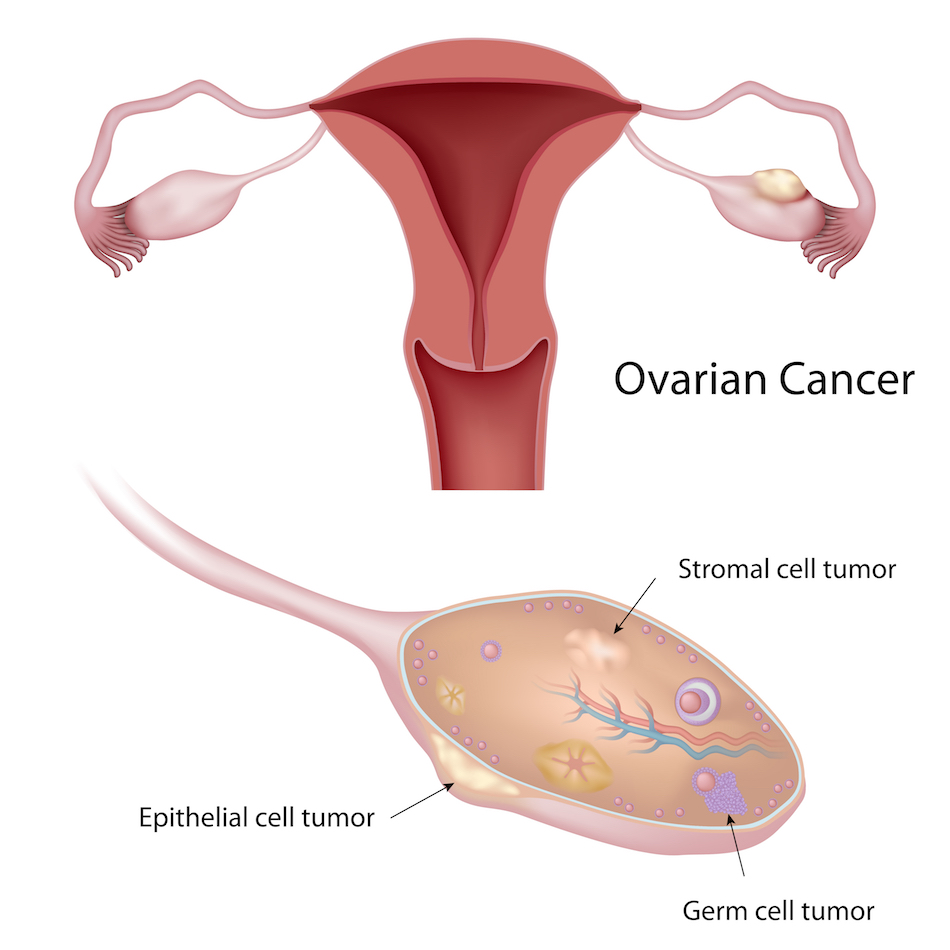
Ovarian cancer originates in the cells of the ovary. A cancerous (malignant) tumour is a cluster of cells that can invade and destroy the surrounding tissues. It can also spread (metastases) to other parts of the body. Ovarian cancer tumours are classified according to the type of cells in which the cancer appears.
Epithelial carcinoma of the ovary originates in the epithelial cells. It is the most common type of ovarian cancer. Serous carcinoma is the most common type of epithelial carcinoma of the ovary.
Stromal tumours originate in stromal cells. Of the stromal tumours that may be malignant, granulosa tumours are the most common type.
Germ cell tumours appear in the germ cells. Of all ovarian tumours, the most common type is the mature cystic teratoma (dermoid cyst). In general, it is not cancerous. The most common type of cancerous germ cell tumour is dysgerminoma.
Primary peritoneal serous carcinoma can occur in the peritoneum, the membrane that lines the walls of the abdomen and pelvis. It is similar to epithelial ovarian cancer, but there is very little or no cancer in the ovary and it is not clear where the cancer originated.
Symptoms:
• Abnormal vaginal bleedinga
• Palpable mass in the pelvis
• Bladder disorders
• Constipation
• Tiredness
• Weight loss
• Difficulty breathing
• Pain during sexual intercourse
• Sensation of pressure in the pelvis or abdomen
It is difficult to give an accurate estimate of the cost of treatment without first reviewing your medical file. Doctors and specialists from the MEDICAIM network will examine your file before returning to you with a treatment plan. Do not hesitate to contact a MEDICAIM advisor: he will assist you in obtaining a quote and a personalized estimate.
Contact a MEDICAIM careteam assistant by clicking on this link or by phone at (+33) 9 72 39 70 70.
Duration of hospital stay
5 to 8 days.
Depending on each patient, the duration varies.
Average length of stay
2 to 3 weeks.
The length of stay varies according to the patients.
Several stays may be necessary.
Every year, nearly 11 million patients go abroad in search of medical care. At MEDICAIM, we provide our patients with access to the best hospitals and doctors around the world. Contact us to learn more about your treatment options.
Ask for your free quote abroad
Start your medical stay by requesting a quote. Our customer service department will help you find the clinic that best suits your needs and get you a quote.
The doctor will start the consultation with a clinical interview associated with different examinations:
• Clinical examination. the onset of Pain is first assessed by a Clinical examination to assess the characteristics of the Pain and the symptoms associated with it.
• Medical imaging examination. Depending on the suspected or proven pathology, additional examinations may be carried out such as ultrasound, radiography, CT scan, laparoscopy, MRI.
• Coelioscopy. This examination is an endoscopic technique that allows access to the abdominal cavity without opening the abdominal wall.
• Biological examination. Blood tests can be carried out to detect tumour markers, for example.
Your doctor may also ask you about your family history and perform a physical examination.
The oncologist will establish a treatment plan based on these results.
If you have ovarian cancer, the doctor will develop a treatment plan especially for you. The doctor takes the following elements into consideration:
• Stage
• Rank
• Type of tumor
• If you want to have children one day
• You may be offered one or more of the following treatments for ovarian cancer.
Surgery:
Surgery is the main treatment for ovarian cancer, regardless of stage and type.
The most common operation performed is total hysterectomy with bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy. During surgery, the uterus, ovaries and fallopian tubes are removed. Sometimes the surrounding lymph nodes are also removed.
Salpingo-oophorectomy can be unilateral (i.e., the ovary and fallopian tube are removed on one side only) or bilateral (i.e., both ovaries and fallopian tubes are removed).
During tumor reduction surgery, as much of the cancer as possible is removed from the abdomen.
In a cystectomy, only the cyst containing the tumor is removed and the rest of the ovary is left intact.
Some surgical procedures can be used to relieve the symptoms of advanced ovarian cancer.
General anesthesia
The operation lasts between 40 and 90 minutes.
Chemotherapy:
Chemotherapy is available before or after surgery to treat certain types and stages of ovarian cancer.
Chemotherapy can also be used to relieve pain or to control symptoms of ovarian cancer (referred to as palliative chemotherapy).
Hormone therapy:
Some women with low-grade ovarian cancer may receive hormone therapy rather than chemotherapy after surgery.
Targeted treatment:
Some women with epithelial ovarian cancer or advanced primary peritoneal carcinoma may receive targeted treatment with or without chemotherapy.
Radiotherapy:
Radiotherapy can be used after surgery if a woman cannot receive chemotherapy because of her age or health problems.

In the event that the patient undergoes surgery, after the operation, the patient remains in intensive care for a few days and then returns to the department in which he or she was admitted. Hospitalization often lasts two to three weeks.
It is advisable to avoid any significant effort or travel within the first month after the procedure.
A chest tube is placed at the end of the procedure.
There are frequent small bleeding and variable losses during the first month. This is due to the points in the vagina and scarring, and transit can sometimes resume slowly.
Risks:
• Phlebitis
• Pulmonary embolism
• Urinary infection
• Hematoma
After the treatment, the specialist determines with the patient his/her follow-up.
The total duration of treatment varies according to each patient.
**Once the cancer treatment is completed, a follow-up is performed to: **
• Monitor the response to treatment of the treated patient
• Identify any long-term side effects
• Monitor the general well-being of the treated person
• Check for any signs of cancer recurrence
• Monitor for the absence of the development of A second cancer.
Some complex diseases such as cancer can lead some patients to seek a second medical opinion. Almost 50% of patients using the second medical opinion have seen their treatment options evolve. Seeking a second medical opinion is perfectly legitimate when faced with a serious illness.
Click here to find out more about the second MEDICAIM medical opinion
MEDICAIM is looking for the best specialists for you and we will offer you several renowned doctors.
MEDICAIM organizes your entire stay for you: post-operative nursing care, biological follow-up, therapeutic, nutritional and psychological support.
Any additional questions? Ask your doctor about it: careteam@medicaim.com
Some needs and conditions are more complex than others. In case of doubt, please send us additional information to establish a customized quote.
Ask for a quoteCertains besoins et pathologies sont plus complexes que d’autres. En cas de doute, faîtes-nous parvenir des informations complémentaires pour établir un devis sur-mesure.
Demander un devisEntrust us with your medical file and it will be examined by a specialist doctor. The goal?
Allow you to evaluate all your treatment options.